Egocentric Social Network Structure, Health, and Pro-Social
Using a population-based, panel survey, we study how egocentric social networks change over time, and the relationship between egocentric network properties and health and pro-social behaviors. We find that the number of prosocial activities is strongly positively associated with having more friends, or an increase in degree, with approximately 0.04 more prosocial behaviors expected for every friend added. Moreover, having more friends is associated with an improvement in health, while being healthy and prosocial is associated with closer relationships. Specifically, a unit increase in health is associated with an expected 0.45 percentage-point increase in average closeness, while adding a prosocial activity is associated with a 0.46 percentage-point increase in the closeness of one’s relationships. Furthermore, a tradeoff between degree and closeness of social contacts was observed. As the number of close social contacts increases by one, the estimated average closeness of each individual contact decreases by approximately three percentage-points. The increased awareness of the importance of spillover effects in health and health care makes the ascertainment of egocentric social networks a valuable complement to investigations of the relationship between socioeconomic factors and health.
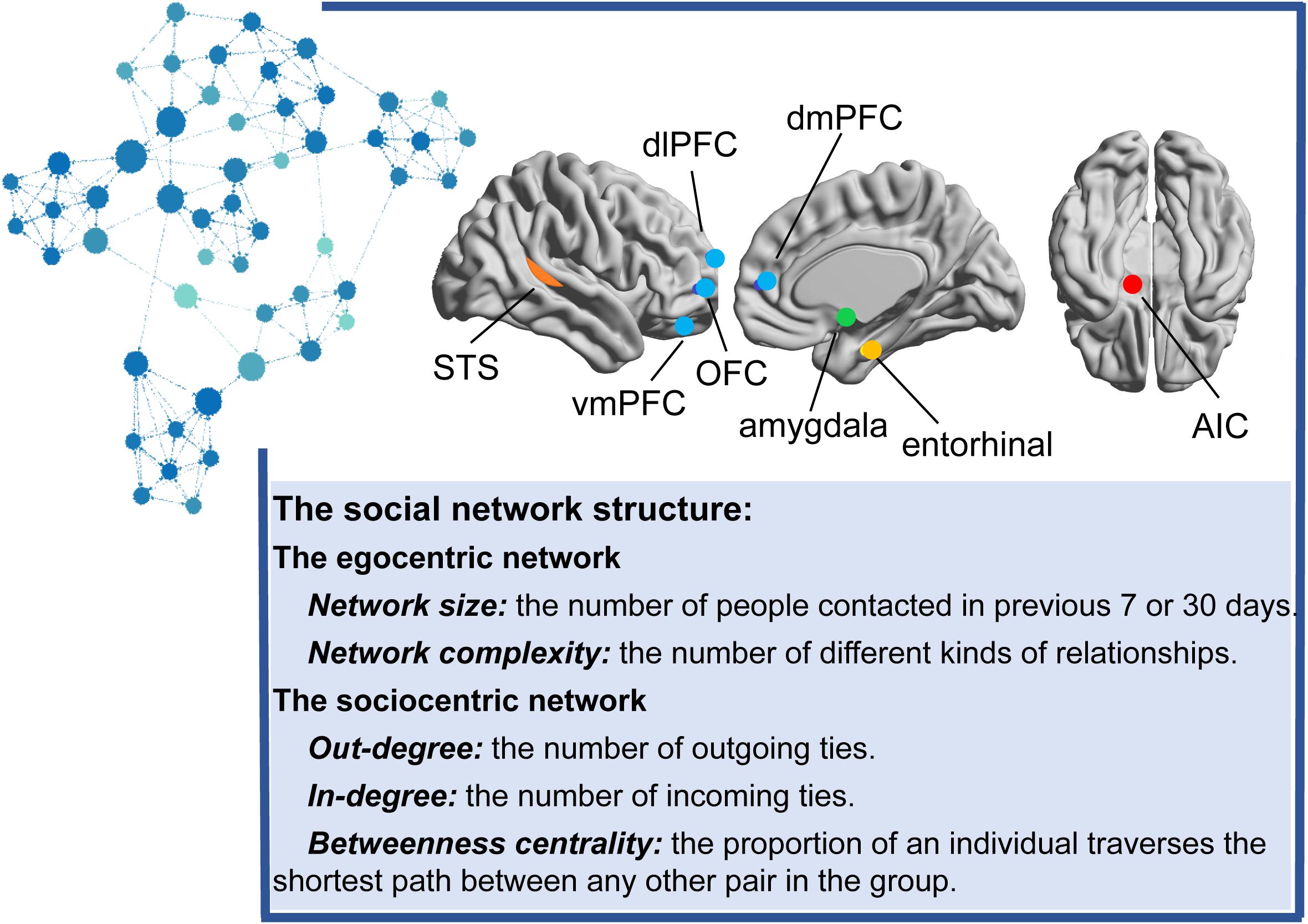
Frontiers Neurobiological Bases of Social Networks

The Niakhar Social Networks and Health Project - Methods X

Exploring Naturalistic Diffusion of an Evidence-Based Mental
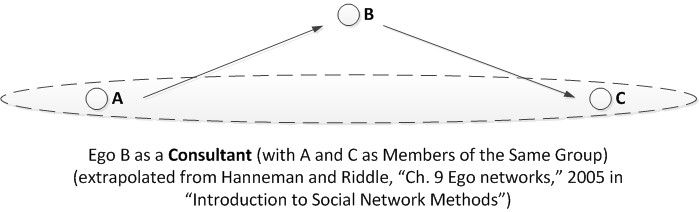
Building and Analyzing Node-Link Diagrams to Understand Social Networks
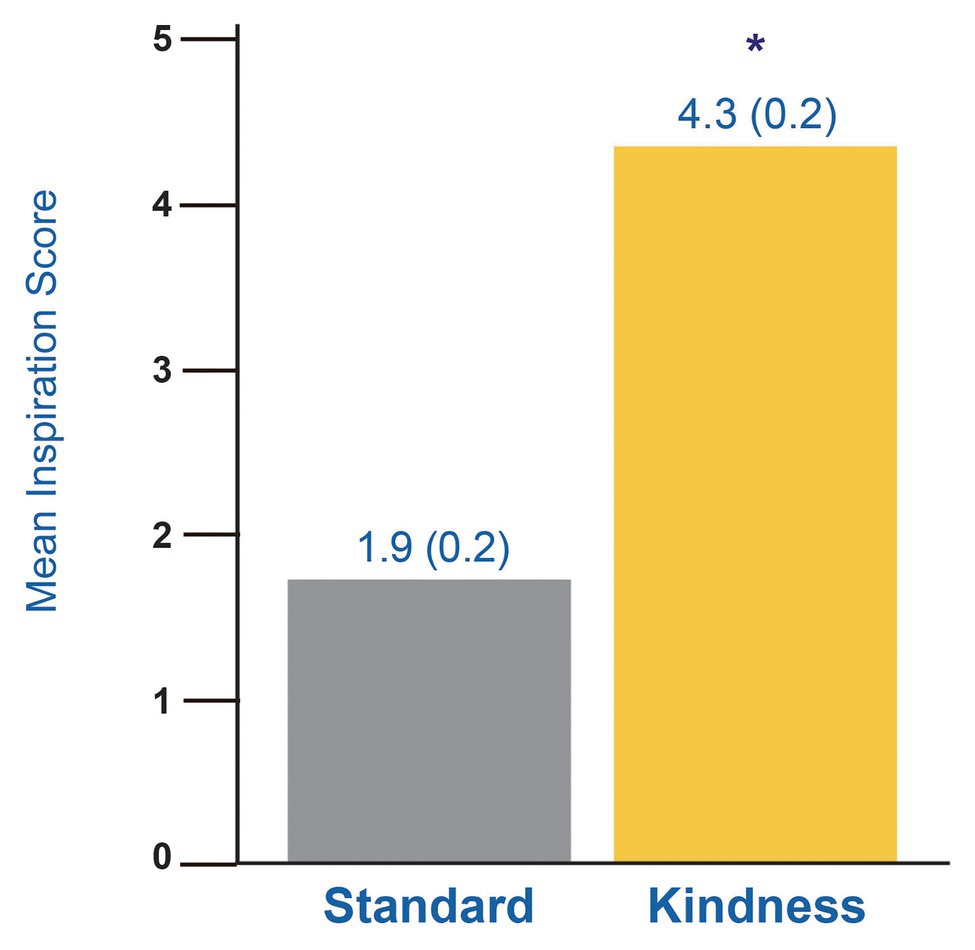
Frontiers Kindness Media Rapidly Inspires Viewers and Increases

Social network analysis to study health behaviours in adolescents

Exploring the organisational structure of networks for exercise oncology provision: a social network analysis of OnkoAktiv, BMC Health Services Research

What can egocentric network measures contribute to stated

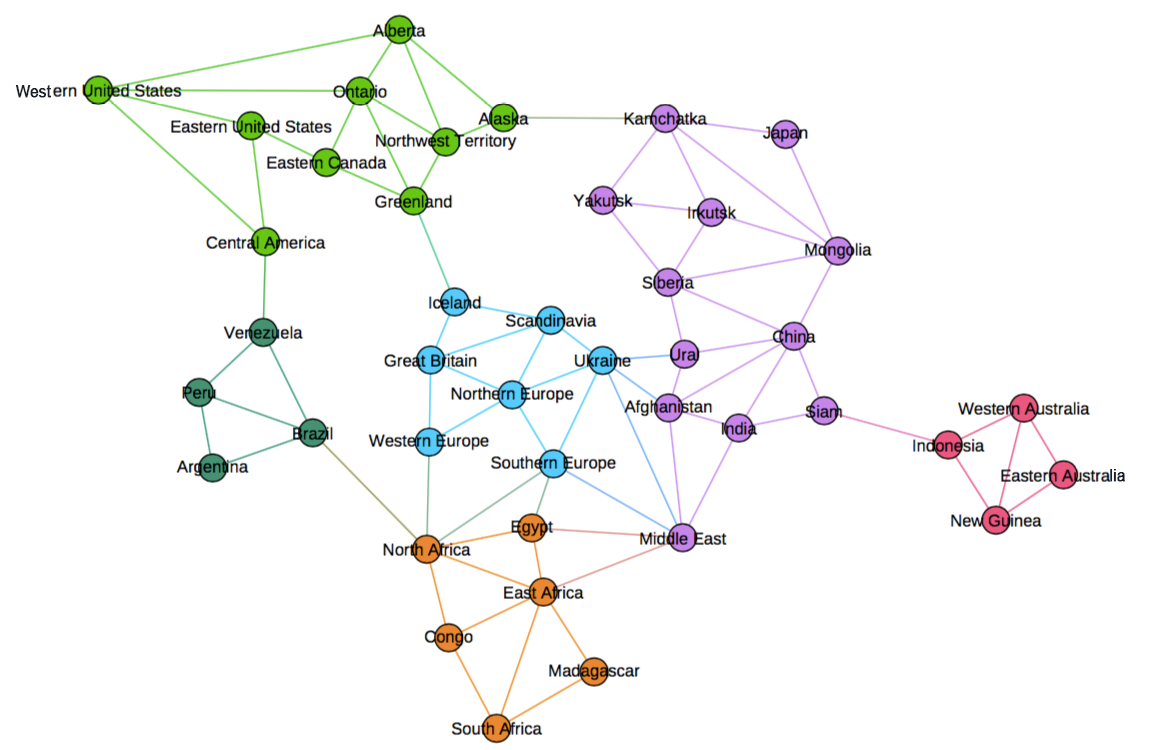
Example of an egocentric network. This example participant responds to
The top six actors in the egocentric network.
Detecting social network effects on willingness to pay for